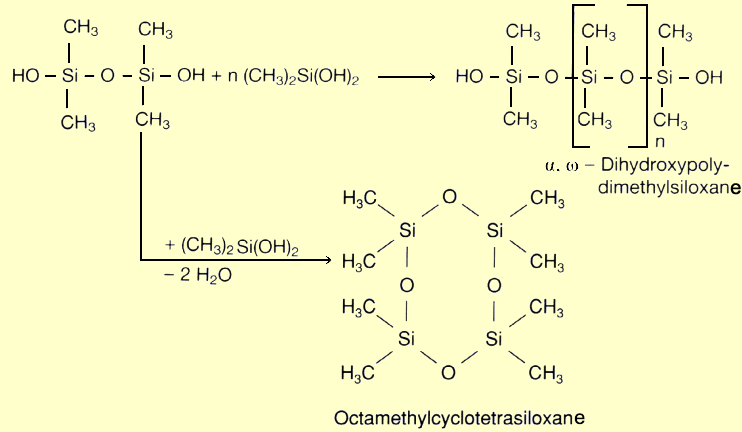
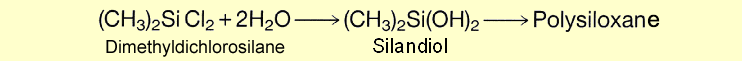Now that the various silane syntheses have been described in detail, this section will illustrate what these precursors are used for. As the title indicates, synthesis is followed by hydrolysis, which is accompanied by polycondensation.
First, the two chlorine atoms are replaced by OH groups, with cleavage of HCl. This is followed by condensation to polysiloxane, with release of water. The HCl gas formed is returned to the loop and converted by reaction with methanol into chloromethane, the raw material for the silane synthesis. An alternative to hydrolysis is methanolysis (methanol used instead of water). The resultant chloromethane is also fed back into the Müller-Rochow synthesis. The name silicone was chosen by analogy with ketone. Admittedly, the ketones are always monomers because of their stable carbon oxygen double bonds. On the other hand, silicones always form oligomeric or polymeric structures. Dimeric silicones can only be obtained under special reaction conditions.
Dichlorodimethylsilane is the most important starting material for the manufacture of silicone fluids, silicone emulsions and silicone rubber, as they are all derived from linear polysiloxanes. Silicone resins, by contrast, are made from trichloromethylsilane. It forms a three-dimensional network during polycondensation. Monochlorotrimethylsilane plays a crucial role as chain stopper in polycondensation. Since it has only one chlorine atom that can be substituted, it serves as the terminal member of a polysiloxane chain. |
|||||||||||||
| | Home | Wuppertal University | WACKER | Didactic Dept. | Info | Experiments | Media | Work Group | Feedback | Order CD-ROM | |