 |
Burning of Liquid Silicones |
 |
  1
Materials, Chemicals, Time Needed 1
Materials, Chemicals, Time Needed |
 |
|
One ignition and burning operation lasts about 5 minutes
because the metal plate has to heat up first.
|
 |
  2
Procedure and Observations 2
Procedure and Observations |
 |
Remove flammable materials from the immediate
vicinity because a naked flame is used.
The Teclu burner heats
the bottom of the metal plate on the tripod very efficiently.
When the plate is hot, pour 1 to 3 drops of
the silicone onto the middle of it from above. |
 |
 |
 |
Then step back. When the
flame has extinguished, the experiment can be repeated. Should
the silicone fluid emit vapors instead of igniting spontaneously,
light the
vapors directly with the flame and then continue heating
the plate from beneath. The heated silicone fluid emits
some vapor before burning with a glaring white flame (left
picture). The fire lasts for 5 to 20 seconds. Whitish gray
flocs rise up out of the ashes. Some silicone fluids only
burn when ignited directly with the burner flame. A fine
white ash is left behind on the metal plate (right picture). |
|
 |
  3
Discussion of Results 3
Discussion of Results
|
 |
At elevated temperatures in an adequate supply of air, methylsilicones
burn to form a silica with a very large surface area, water
and carbon dioxide. In the experiments, the flame sometimes
looks yellowish and the ash is not quite white. This indicates
that combustion did not quite go to completion. The equation
for complete combustion is:
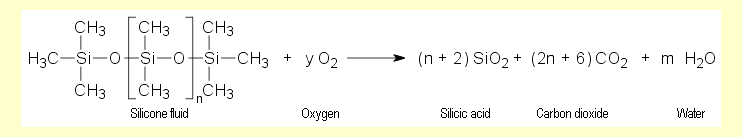
The composition of the silica only approximates to the formula SiO2.
We are dealing here with neither discrete SiO2 molecules nor quartz,
but rather with tiny grains in which each silicon atom is tetrahedrally
surrounded by four oxygen atoms and each oxygen atom forms a bridge between
two silicon atoms. The oxygen atoms at the edge of a grain each have
one bond to a hydrogen atom. |
 |
  4
Tips and Comments 4
Tips and Comments
|
 |
- Combustion of silicones is easy to perform and may be done
during preliminary studies of different polymers as it provides
information about elemental composition.
- For a discussion of
combustion, see page 7 of “Silicone
fluids, resins and rubbers worksheets”.
|
 |
  5
Supplementary Information 5
Supplementary Information
|
 |
| The worksheets mentioned above
contain supplementary information on, for example, enthalpies
of combustion, which can be useful for comparing combustion of
silicones with other polymers. |
 |
 |